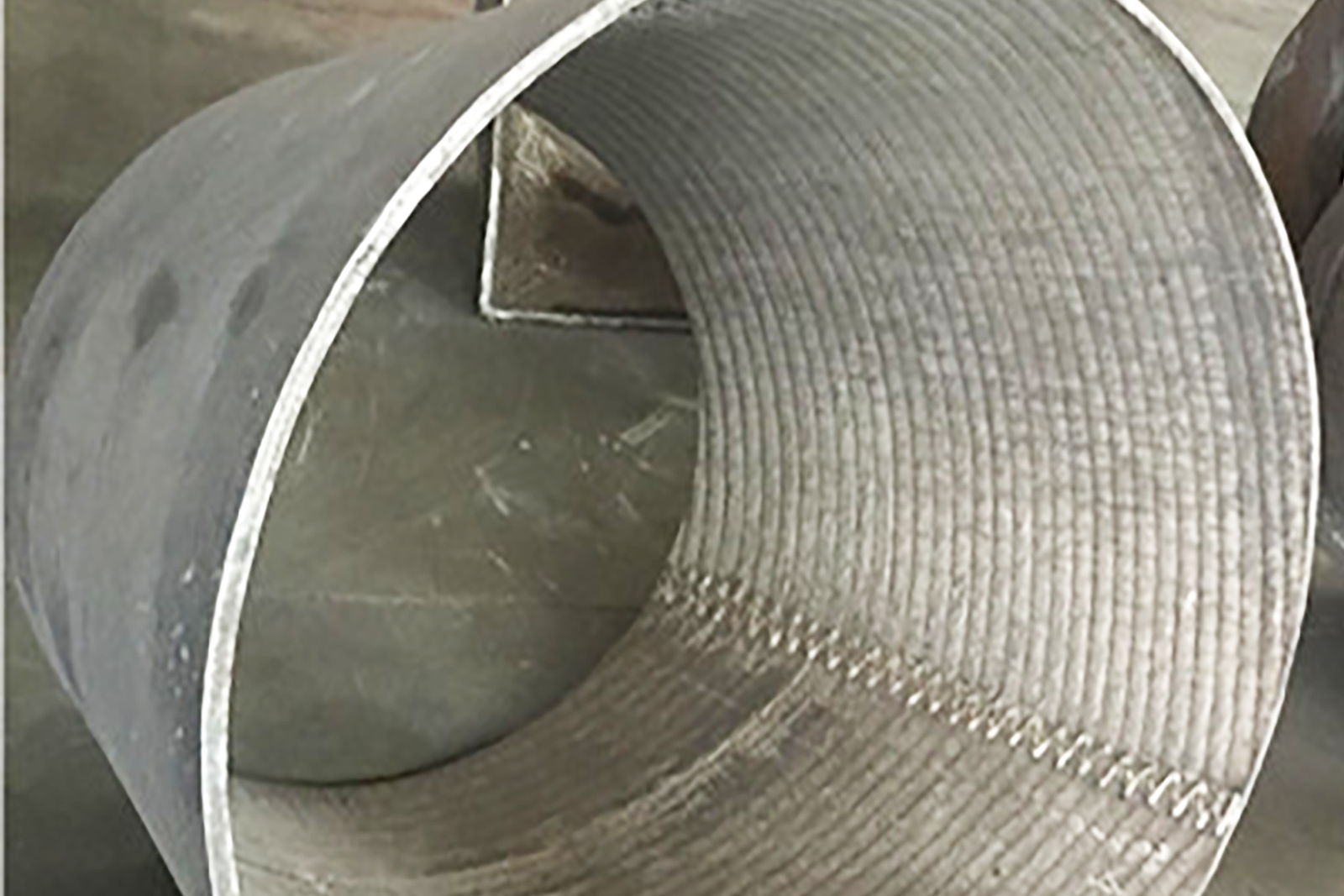
Kooben composite wear-resistant steel plates

In the 1960s, the United States, Britain, Germany and other countries began developing and manufacturing composite wear-resistant steel plates (also known as wear plates). The world’s first composite wear-resistant steel plate was manufactured by TAPCO Corporation in the United States using surfacing technology. By studying foreign technologies, Beijing University of Technology had realized Chinese development of technology used to manufacture Composite wear-resistant steel plates in 1987. We then manufactured China’s first commercialized composite wear-resistant steel plates in 1991 by working with the Beijing University of Technology.
Advantages of using composite wear-resistant steel plates
- Reduction of maintenance costs
- Reduction of downtime and increased equipment availability
- Reduction of wear and tear that reduces equipment capacity and increases power consumption
- Substantial reduction of wear, damage, and flaking that contaminates the environment and leads to high labor costs for clean-up
Microstructure
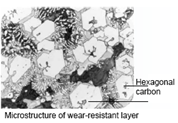
Our third-generation surfacing technology prepares a wear-resistant layer with a thickness of 1/8 to 5/8 inch (3-15 mm). The matrix of the wear layer is composed of eutectic cementite, alloy martensite, and retained austenite. The carbon content of the main component is 4-5%, and the Chromium content is 25-30%. The volume fraction of Cr7C3 carbide in the metallographic structure reaches more than 50%. The dispersed hexagonal carbide, which is the hard phase of the wear-resistant layer, has a hardness of up to 1800 HV.
Mechanical properties
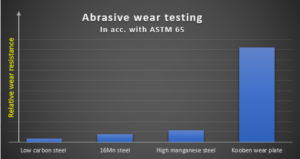
The hardness of the wear-resistant layer of the composite wear-resistant steel plate was shown to be greater than 60 HRC by independent laboratory testing. Experimental data show that the wear resistance of our composite wear-resistant steel plate is 20-25 times that of low carbon steel, 10-12 times that of 16Mn steel, and 5-8 times that of high manganese steel.
The substrate of our composite wear-resistant steel plates is a tough low-carbon steel (such as Q235). During use, the wear-resistant layer resists abrasion of the wear medium, and the substrate bears the load of the medium. Therefore, our composite wear-resistant steel plates have good impact resistance. They can be used in high drop impact and wear situations, such as hoppers for conveyor systems.
Bonding
The wear-resistant layer and the substrate are metallurgically bonded. This bond is strong and prevents peeling.
Heat resistance
The wear plate is made of alloys, so it has a maximum working temperature of 400°C or less. If you need to resist higher temperatures, Kooben Technology USA can customize the composition of the hardfaced layer to meet your requirements.
Corrosion resistance
The wear layer contains a high percentage of chromium, which has the properties of chromium stainless steel and can protect products susceptible to corrosion.
Machining
Our composite wear-resistant steel plates can be cut, bent, holed, welded, and plug welded. Other types of machining are also possible.

Cutting
The entire composite wear-resistant steel plate can be cut using a plasma cutter to produce the desired shape and size.
Holing
Plasma cutters can be used to make holes in composite wear-resistant steel plates. Manual plasma cutting and numerical control plasma cutting can be used; the method chosen should be appropriate for the user’s precision requirements.
Welding
Multiple sheets of composite wear-resistant steel plate substrate can be welded together to increase area. Composite wear plates can also be flat.
Our composite wear-resistant steel plates can be connected with other workpieces using welding, face welding or back welding bolts. They are suitable for on-site construction.
Bending
Through cold forming, the composite wear-resistant steel plates can be bent into the desired arc or cylinder.

Dimensions
The thickness of the substrate and wear layer can be adjusted according to customers’ operating conditions and requirements.
| Grade | Substrate thickness (mm) | Wear-resistant layer thickness (mm) | Hardness (HRC) | Plate dimensions: ft (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB6+4 | 6 | 4 | <60 | 5x20 (1500 x 6000) |
| KB8+4 | 8 | 4 | ||
| KB10+5 | 10 | 5 | ||
| KB10+8 | 10 | 8 | ||
| KB12+5 | 12 | 5 | ||
| KB15+8 | 12 | 8 | ||
| KB15+15 | 15 | 15 | ||
| KB10+10+10 | 10 | 10 (double-sided) |
Typical applications
| Cement industry | Mill feeders | Fan blades and liners | Crusher beams and linings | Excavator buckets |
| Mill liners | Pump casing | Whirlwind dust collectors | Screw conveyors | |
| Hoppers | Powder separator blades and liners | Chutes | Liners | |
| Power industry | Coal mill barrel liners | Fan impeller shells | Dust collector inlet flues | Ash conduit |
| Bucket wheels and liners | Separators and connecting pipes | Coal lining boards | Burner fronts | |
| Fuel falling coal and funnels | Air preheater brackets | Separator blades | Coal pipeline liners | |
| Coal industry | Shearer drums | Shearer shoes | Chute liners | Spiral chutes |
| Coal falling buckets | Bunker walls | Sieve plates and screens | Scraper conveyors | |
| Other industries | Glass factory material mixing systems | Concrete mixing plants | Brick factory molds | Coking plant conveyor chutes |
| Port material handling systems | Mine dump truck liners | Ship unloader grabs | Three links and elbows |


